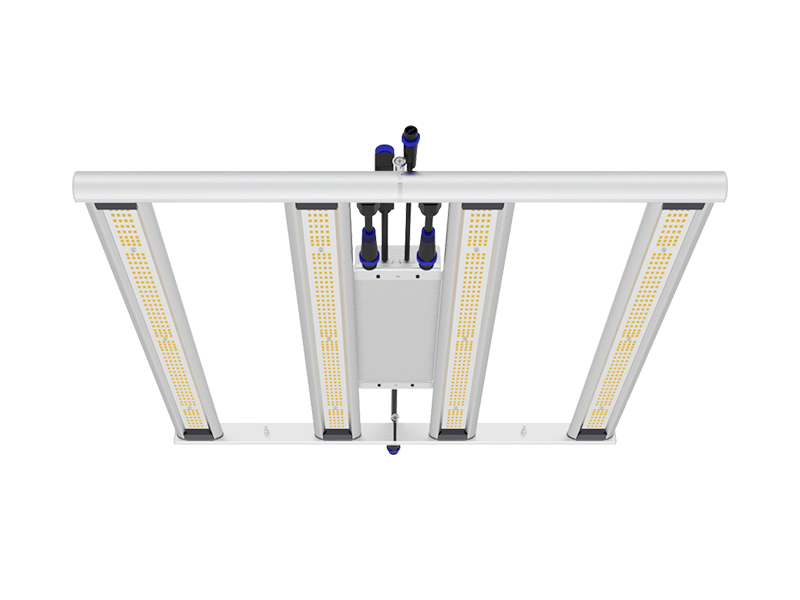
Light is a very important thing for plants, which not only rely on light for photosynthesis, but also have their own unique effects on the growth and development of plants at different wavelengths. Red, blue, ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), and far-red (FR) are some of the most critical spectral types. They play an integral role in promoting plant growth, flowering, fruit ripening, and pest and disease defense. Today, we're going to take a closer look at the effects of these different spectrums on plant growth~
Red light: Promotes flowering and fruit ripening
The wavelength of red light (640-660 nm) is essential for plant growth, especially during flowering and fruit ripening. Red light can penetrate deep into the chloroplasts of plants, effectively promote photosynthesis, and accelerate the growth rate of plants. In most plants, especially flowers and certain fruits and vegetables, red light also promotes flowering and fruit ripening.
In practical applications, by increasing the irradiation of red light, the speed of plant growth can be accelerated, and the time from sowing to harvesting can be shortened. For example, tomatoes and peppers ripen faster and are more colorful when exposed to more red light.
Blue light: Promotes leaf development and photosynthesis
Blue light wavelengths (450-460 nm) also play an important role in plant growth. Blue light is essential for the proper growth of plants, as it promotes leaf development and the efficiency of photosynthesis. In some plants, blue light can also affect the timing of flowering and the shape of flowers.
In greenhouses or indoor growing, the application of blue light is particularly important. For example, at the seedling stage, blue light promotes the healthy growth of leafy plants, such as lettuce and spinach, and prevents overgrowth. For some ornamental plants, proper blue light exposure can also increase their ornamental value, such as promoting more vivid colors of certain flowers.
UV (Ultraviolet Light): Promotes plant growth and protection from diseases
When we talk about ultraviolet (UV), it is actually a type of light that is invisible to the human eye, and its wavelength is shorter than the violet light we can see. Ultraviolet light can be divided into three categories: long-wave ultraviolet (UV-A), medium-wave ultraviolet (UV-B), and short-wave ultraviolet (UV-C).
If plants are exposed to too much ultraviolet (UV-B) light, they will become shorter, their leaves will shrink, and more fine hairs will grow on the leaves. Not only that, but the substances stored in the plant's body will increase, and the chlorophyll will also increase. This makes the color of the plant look particularly vibrant, like putting on a bright coat for the plant.
Ultraviolet light (UV-A) is an incentive for plants to increase yields and promote the production of proteins, sugars and acids in plants. If you shine the seeds with this light, it can also help the seeds germinate better.
Short-wave ultraviolet (UV-C) is like a protective shield, although it has a certain inhibitory effect on plant growth, it can prevent overgrowth of plants, and it also has a bactericidal effect, which can help reduce the chance of plant disease.
IR (infrared): regulates plant temperature and adapts to the environment
Infrared ray (IR) is what we usually call "thermal radiation". When we feel warmth in the sun, or comfort near a hot water bottle, that's infrared rays’ influence. Infrared rays are also important to plants, as they are like to be given a warm hug.
Control the "body temperature" of plants: Just like we humans need to maintain a suitable body temperature, plants also need a suitable temperature to grow. In a greenhouse, using infrared rays to heat is like turning on a heater for plants, especially in winter or cold weather, helping plants stay warm and promoting their growth.
Help plants better adapt to the environment: Infrared rays can also help plants regulate water evaporation. Just like we sweat, plants regulate body temperature by evaporating water from their leaves. Proper infrared light can help plants better control this process, allowing them to grow better in environments that are too hot or too dry.
FR (far red light): promotes plant growth
Far red light (FR) is like a growth guide for plants. It helps plants decide how to grow, such as making them taller or spreading their leaves wider. FR has a significant impact on the photoperiodic response of plants, especially in flowering plants.
In some cases, appropriate FR exposure can promote faster plant growth, especially in those plants that require longer photoperiods. For example, for some flowers that require long days, FR irradiation can promote them to enter the flowering stage faster.

Different spectrum have different effects on plant growth. VANQ's LED grow lights can customize full-spectrum lighting according to the needs of plants, providing an optimal growth environment for plants, promoting growth and increasing yields. Click the dialog box below to contact us~