We may have heard of the concept of PPFD when buying plant lights or planting.
So what exactly is PPFD?
What’s the best ppfd for flowering and best ppfd for veg?
Let’s take a deeper look today.
1.What’s the PPFD?
PPFD refers to Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density, which measures the intensity of light per unit area in micromoles per square meter per second (μmol/m²/s). For plants, light is the source of energy for photosynthesis, and the level of PPFD directly affects the growth rate and health of plants.
To explain it simply, it is actually a ruler to measure the intensity of light, to see how many photons there are per square meter per second.
2. The ppfd for vegetative growth

The PPFD (photon flux density) requirements of plants vary depending on the type of plant and the growth stage. Generally speaking, different types of plants have different PPFD requirements during their growth cycle.
the best ppfd for veg:
The growth period is a critical stage in the life cycle of plants. Plants need sufficient light to support leaf growth and plant structure development. Fruit and vegetable plants such as tomatoes and cucumbers require 200 to 400 μmol/m²/s PPFD during the growth period, depending on the type and variety of the plant.
At this stage, proper light can promote the healthy growth of plants, increase leaf area, and thus enhance the efficiency of photosynthesis.
the best ppfd for flowering
Flowering is another critical period in the plant growth cycle, and plants need higher light to promote the formation of flower buds and extend the flowering period. Fruit and vegetable plants such as tomatoes and cucumbers require 300 to 600 μmol/m²/s PPFD during the growth period.
High light demand plants such as cannabis may need 800 to 1200 μmol/m²/s PPFD during the flowering period to ensure the healthy development of flower buds and high-quality yields.
Here are some approximate PPFD ranges for some common plants during the growing and flowering stages:
leafgreen plant(such as Chinese cabbage, spinach):
Vegetative phase:100-300 μmol/m²/s
Flowering time:250-400 μmol/m²/s
Herbs (such as coriander, kudzu root, etc.):
Vegetative phase:150-300 μmol/m²/s
Flowering phase:250-400 μmol/m²/s
Fruit and vegetable plants (such as tomatoes, cucumbers, etc.):
Vegetative phase:200-400 μmol/m²/s
Flowering phase:300-600 μmol/m²/s
Potted plants (such as cacti, succulents, etc):
Vegetative phase:50-200 μmol/m²/s
Flowering phase:100-300 μmol/m²/s
Indoor foliage plants (such as spider plants, ferns, etc.):
Vegetative phase:50-150 μmol/m²/s
Flowering phase:100-250 μmol/m²/s
how do you meet with plant needs for PPFD?

To effectively meet the PPFD needs of plants at different growth stages, growers can take the following measures:
Understanding the PPFD Needs of Plants:
PPFD Different plants require different light intensities at different growth stages. To ensure that they can grow healthily, you must first understand the PPFD required by your plants at different growth stages.。
This will not only help you adjust the appropriate light intensity for the plants, but also ensure that the plants get the best light supply at each growth stage.
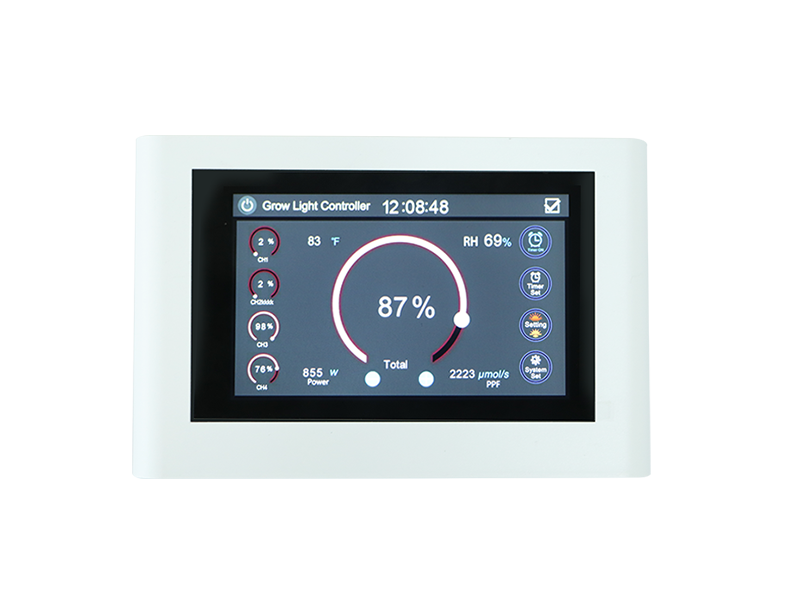
Use a light meter to measure PPFD:
Using a light meter or photon flux density meter can accurately measure the intensity of light and help determine whether the amount of light currently received by the plants meets their needs. This helps to adjust the height and position of the light source to achieve the best lighting conditions.
Control lighting duration and intensity:
Adjust the working time and intensity of the light source according to the needs of the plants and the characteristics of the planting environment. Some plants may require longer sunshine hours, while others require gradual adjustment of light intensity during the growth process.
Provide appropriate light supplementation:
In cases where natural light is insufficient or at night, LED plant growth lights can be used to supplement lighting to ensure that plants receive enough light to promote healthy growth and development.