Jun 06 , 2024
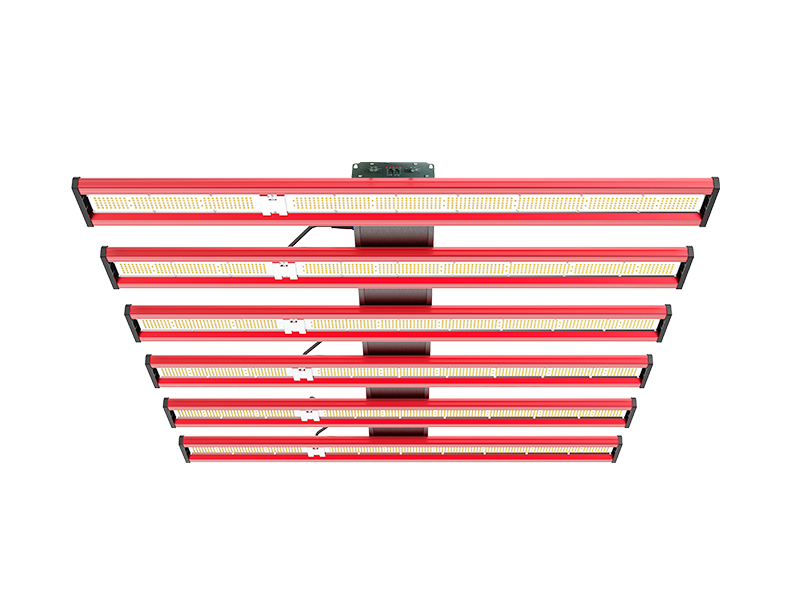
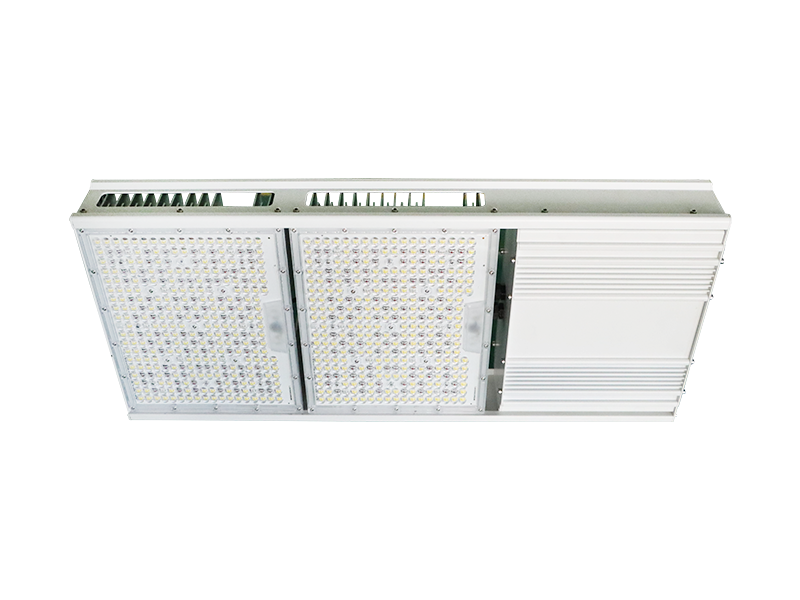
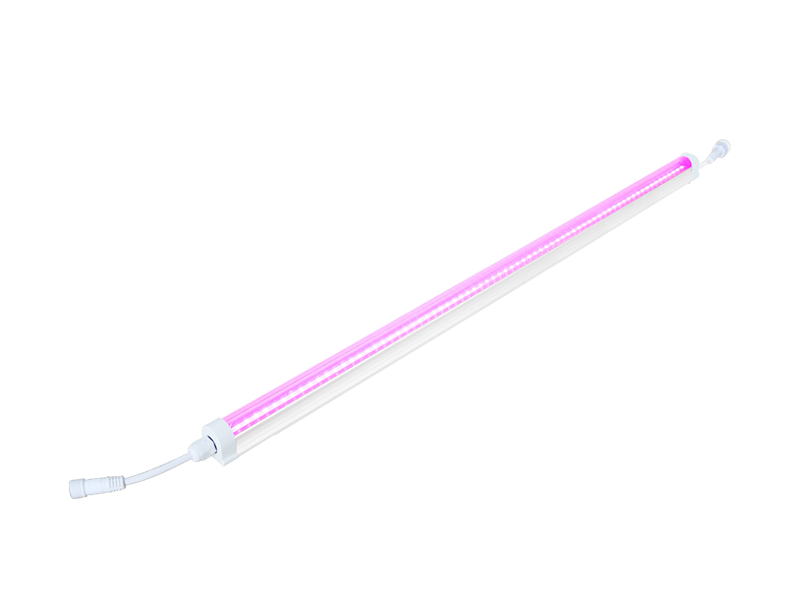
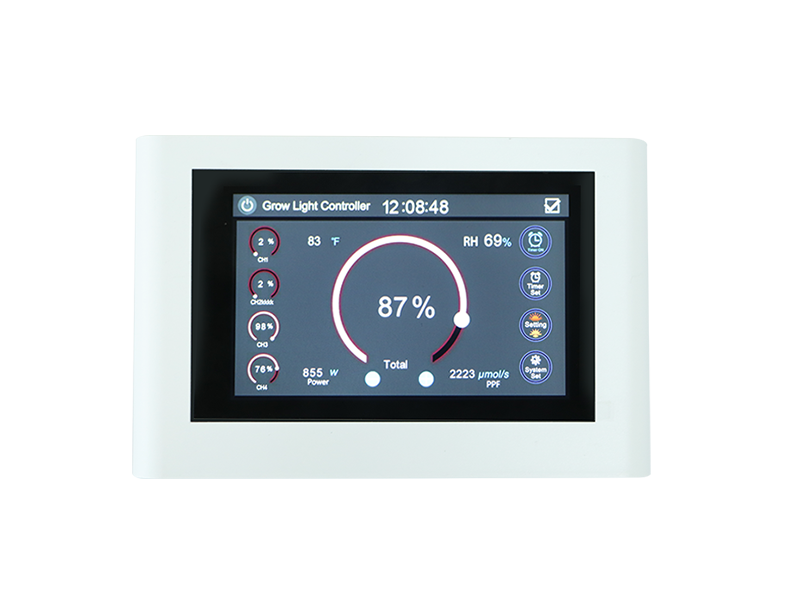
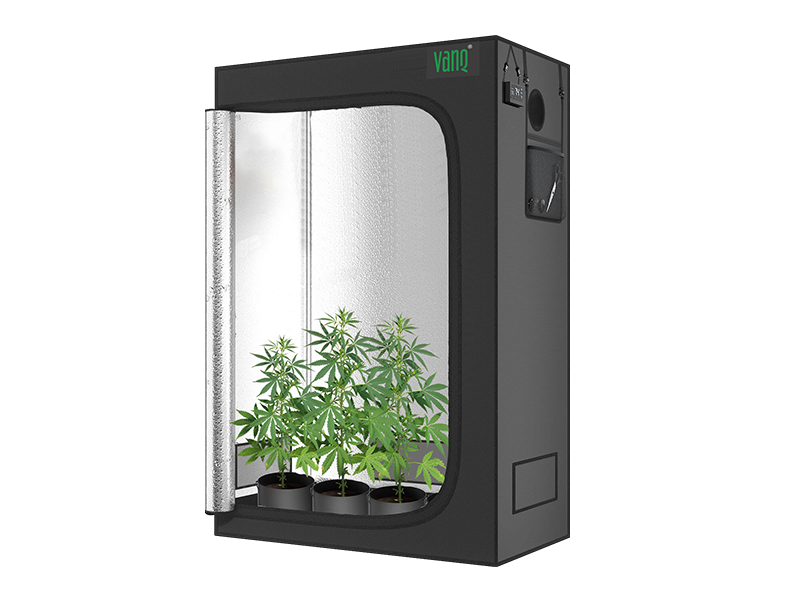
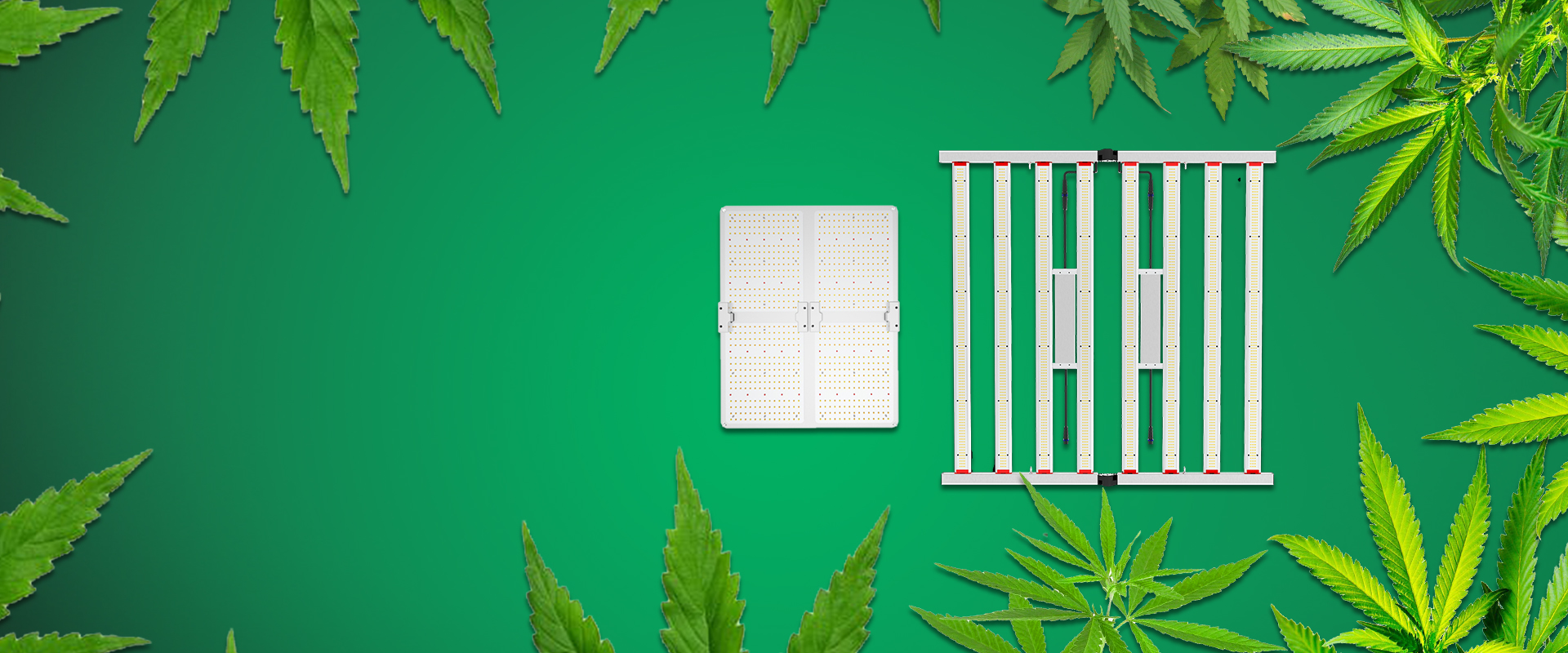
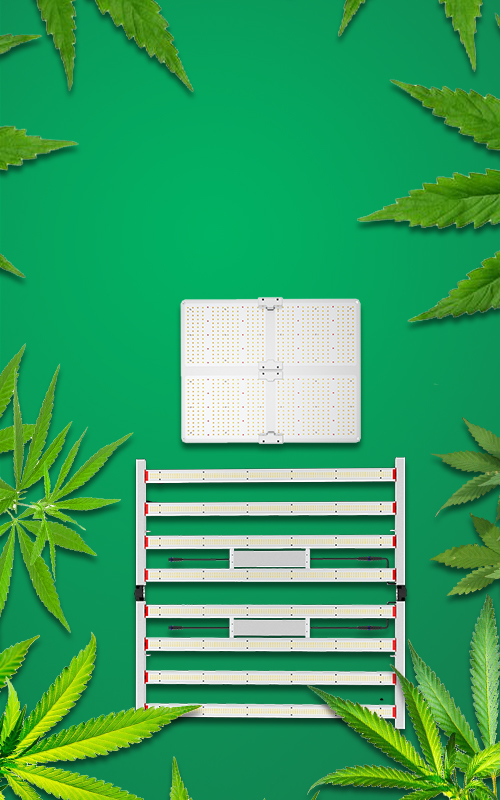
How to Choose the Right LED Grow Light
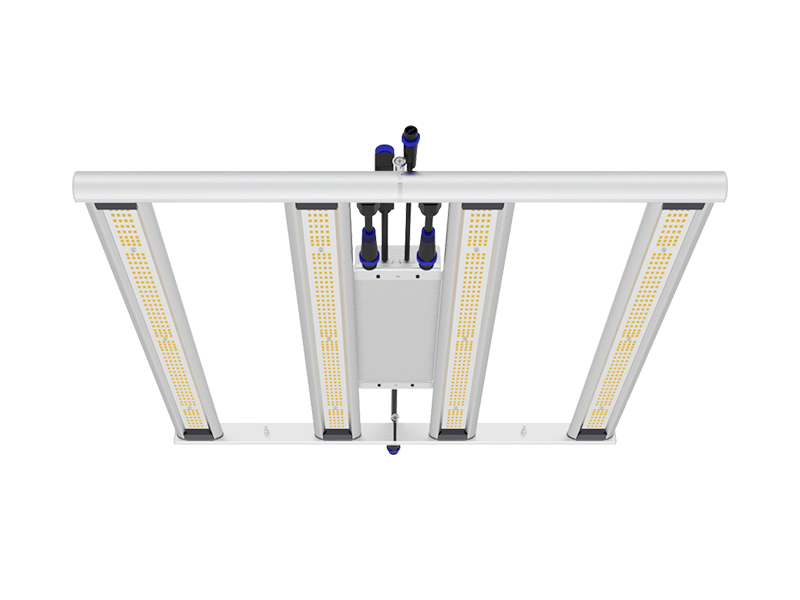
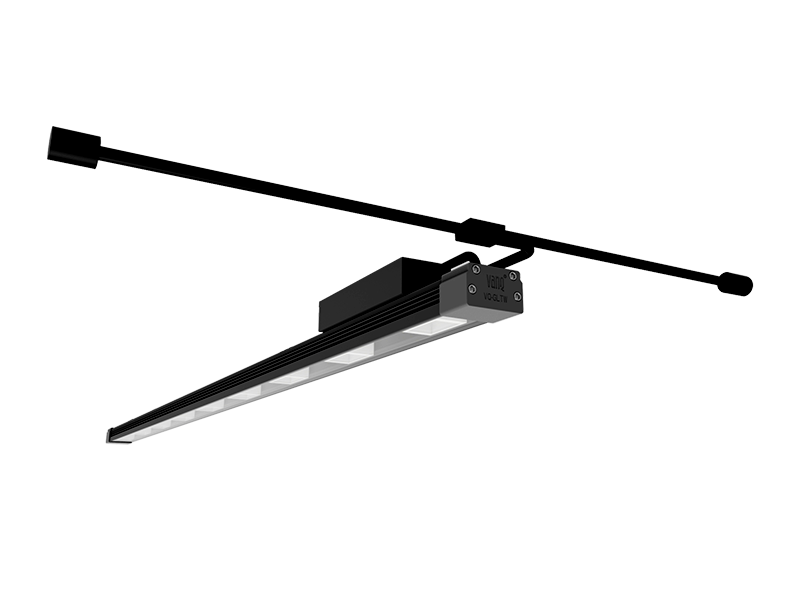
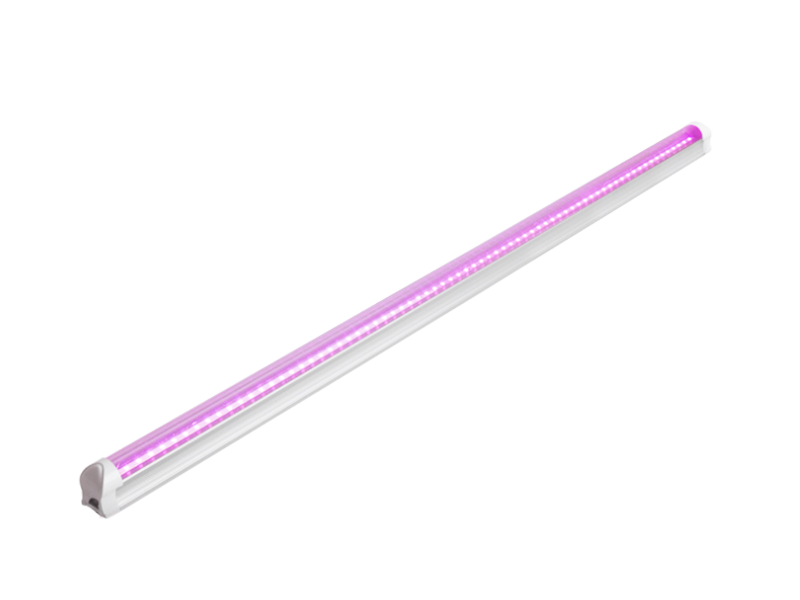
Whether you're growing herbs, vegetables, or flowering plants, choosing the right grow lights can have a big impact on your gardening success. Learn the pros and cons of fluorescent, LED, high pressure sodium, and metal halide lamps.